In our last lesson, we talked about Supervised Learning, where we teach an AI like a student with an answer key. But what happens when there is no answer key? What if you just have a giant, chaotic mess of data and no idea what you’re even looking for?
This is where AI gets to play detective. Welcome to the world of Unsupervised Learning.
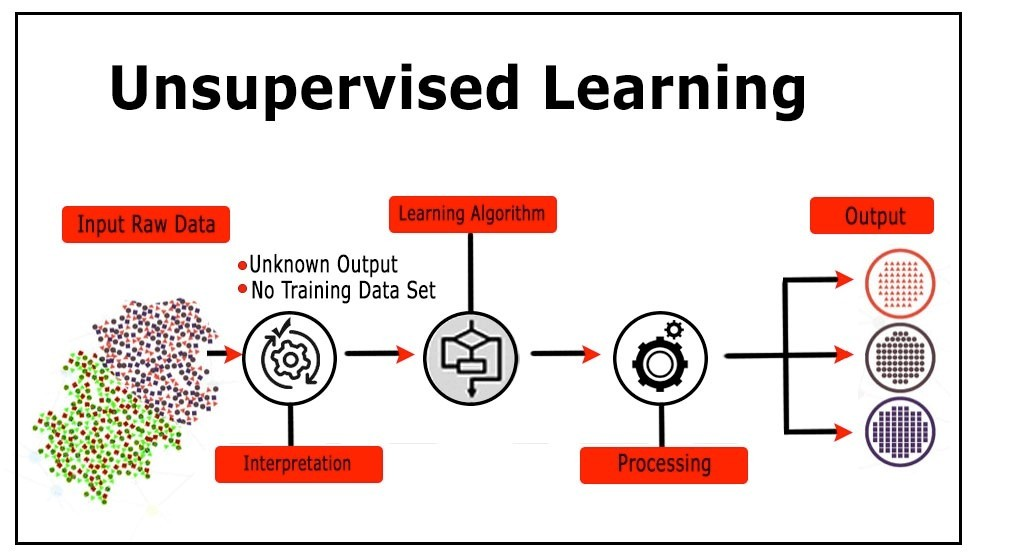
So, what is Unsupervised Learning? It’s a type of machine learning where you give the AI a dataset without any labels or instructions and ask it to find the hidden structures, patterns, and relationships all on its own. It’s not about predicting a known outcome; it’s about discovery.
The Analogy: Picture this: someone dumps a massive, unsorted box of Lego bricks in front of you. There are no instructions. In a supervised world, you’d be told, “Find all the red 2×4 bricks.” In the world of Unsupervised Learning, you’re just told, “Organize this.” You would naturally start making piles of similar colors and shapes, creating groups and finding structure in the chaos. That’s exactly what this type of AI does.
This “figure-it-out-yourself” approach is incredibly powerful and is primarily done using two main techniques.
Technique 1: Clustering (The “Grouping” Method)
Clustering is the most common form of Unsupervised Learning. Its goal is simple: to find natural groups (or “clusters”) within the data, where items in the same group are more similar to each other than to those in other groups.
The AI doesn’t know what the groups are called; it just knows they exist.
Real-World Example: Your Netflix or Spotify Recommendations
Have you ever wondered how streaming services seem to know your taste in movies or music so well? That’s clustering at work.
- They take millions of users and analyze their viewing or listening habits.
- The Unsupervised Learning model then groups users into clusters based on their behavior. It doesn’t know “Cluster A” is “Fans of 90s Action Movies” or “Cluster B” is “Lo-Fi Beats for Studying.” It just knows the people in Cluster A all watch similar things.
- When a new movie is popular with the rest of your cluster, the service recommends it to you, assuming you’ll probably like it too.
Other examples include:
- Customer Segmentation: Businesses group customers by their purchasing habits to create targeted marketing campaigns.
- Image Sorting: Grouping a library of photos into clusters of “beach photos,” “city photos,” and “pet photos” without any pre-existing tags.
Technique 2: Association (The “Frequently Bought Together” Method)
Association is all about discovering interesting relationships between variables in a large dataset. It finds rules that describe how often items appear together. The classic rule it looks for is “if this, then that.”
Real-World Example: The Grocery Store Detective
This is the most famous (and slightly weird) example of an association rule. A major US retailer in the 90s used an Unsupervised Learning model to analyze its sales data. The model discovered a bizarrely strong association: on Friday nights, men who bought diapers also frequently bought beer.
The store’s management had no idea this pattern existed. Acting on this rule, they moved the beer aisle closer to the diaper aisle, and sales of both items reportedly shot up.
This “market basket analysis” is now used everywhere:
- Amazon’s “Frequently bought together” section.
- E-commerce sites bundling products for special offers.
- Medical research finding relationships between symptoms and diseases.
The Detective Work of Unsupervised Learning
So, when would you use this method over its supervised cousin? You use Unsupervised Learning when you don’t have labeled data, or when you don’t even know what you’re looking for. You’re not trying to predict an answer; you’re trying to ask the right questions. It’s a tool for exploration and discovery.
| Supervised Learning | Unsupervised Learning |
|---|---|
| Goal: Predict an outcome. | Goal: Discover a structure. |
| Input Data: Labeled. | Input Data: Unlabeled. |
| Analogy: A student with an answer key. | Analogy: A detective with clues. |
Conclusion: The Unsung Hero of AI
While flashy models like ChatGPT get all the attention, Unsupervised Learning is the unsung hero working behind the scenes. It’s the AI that powers the recommendation engines that run our digital lives and uncovers the hidden business insights that companies use to serve us better (or sell us more beer with our diapers).
It’s proof that sometimes, the most intelligent thing a machine can do is find order in the chaos, all by itself.
Can you think of another place where AI might be grouping or finding patterns without being told to? Share your ideas in the comments!






Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.